I have been wiorking on a project with some fairly strict (to me) lint settings which led me to discovering the inset property.
You CAN teach an old dog new tricks! #
To be fair I am always up for learning new things which is why I still love building web sites - every day is a school day. One thing we create on nearly any project is a card component, and most of the time they have a single clickable link that covers the whole card area.
TRBL spells trouble #
As with borders or padding etc I am very used to chunking out the same code everytime top, right, bottom and left settings to spread the link across the card - but lint said NO! I was forced to investigate the shorthand and must say was surprised it had passed me by for so long.
Can I use it? #
Inset was added to css in 2020 as part of the CSS Logical Properties and Values Level 1 specification and it widely supported (niche browsers aside).

An example card #
My biggest use of the CSS inset property is to make a link cover an entire card component. You want the entire card to be clickable, not just specific elements within it.
Imagine you have a card component with some content, and you want a link inside the card to cover the entire card, making the whole area clickable.
HTML #
<div class="card">
<a href="#" class="card-link"></a>
<h3>Card Title</h3>
<p>This is some card content.</p>
</div>
CSS #
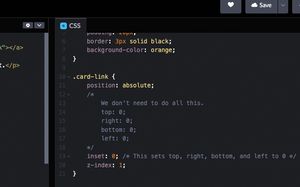
.card {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
position: relative;
width: 300px;
padding: 20px;
border: 3px solid black;
background-color: orange;
}
.card-link {
position: absolute;
/*
We don't need to do all this.
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
*/
inset: 0; /* This sets top, right, bottom, and left to 0 */
z-index: 1;
}
What is going on? #
- position: relative on the .card: This establishes the card as the positioning context for its child elements.
- position: absolute on the .card-link: This allows the link to be positioned absolutely relative to the .card container.
- inset: 0: This is shorthand for top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0;, which makes the link span the entire width and height of the .card component.
- z-index: 1: Ensures the link is on top of the card's content, making the whole card clickable.